TECNOLOGIA E CONTROLLO
15 MAGGIO 2024 – 14:30
Ad Alameda, in California, nei pressi di San Francisco, i funzionari locali hanno ordinato l’interruzione di un esperimento di Geoingegneria solare SRM iniziato nell’aprile scorso, il cui scopo era quello di rendere le nuvole più riflettenti così da diminuire artificialmente il calore prodotto dal sole. L’esperimento, condotto da ricercatori dell’Università di Washington, prevedeva l’irrorazione di minuscole particelle di sale marino sparate a grande potenza dal ponte di volo di una portaerei dismessa, la USS Hornet, attraccata nella baia di San Francisco. La città di Alameda ha però comunicato di aver ordinato ai ricercatori di fermarsi, citando possibili problemi di salute sulla popolazione.
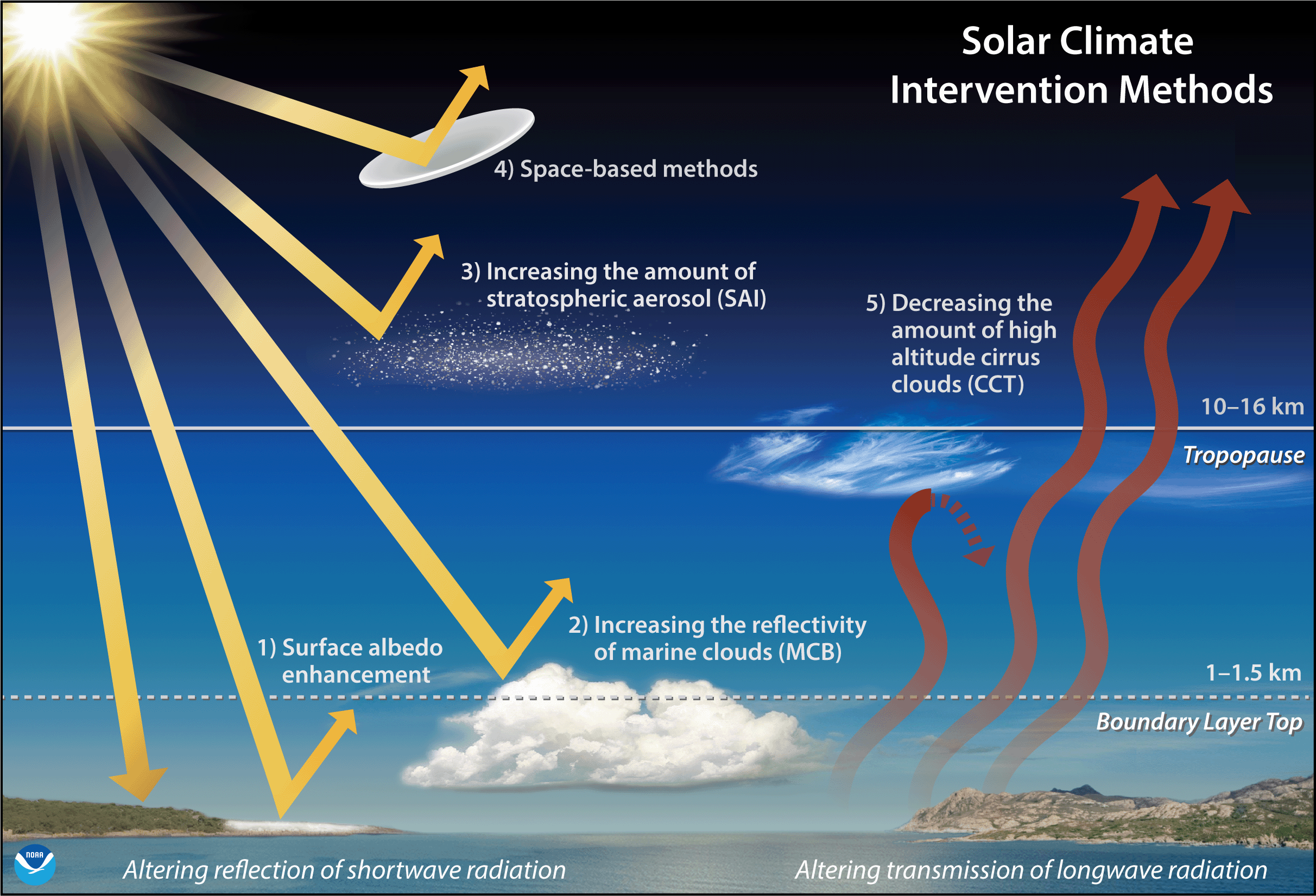
L’esperimento in questione è parte del progetto CAARE (Coastal Atmospheric Aerosol Research and Engagement) ed era stato avviato il 2 Aprile scorso. Rientrava nella categoria che comprende le tecniche e le tecnologie di Geoingegneria che mirano a riflettere la radiazione solare, Solar Radiation Modification (SRM), una di quelle ritenute più controverse per l’impatto invasivo e per le sconosciute conseguenze e ricadute ecologiche e sociali. Gli organizzatori dell’esperimento avevano deciso di mantenere su di esso la massima segretezza per la paura che gli attivisti potessero fermalo, come accaduto già altre volte negli USA. «Il personale della città sta lavorando con un team di consulenti biologici e di materiali pericolosi per valutare in modo indipendente la salute e la sicurezza ambientale di questo particolare esperimento. La città sta valutando i composti chimici nello spray per determinare se sono un pericolo inalati in forma di aerosol da esseri umani e animali, o atterrando a terra o nella baia» è quanto scritto dai funzionari di Alameda. Sarah Henry, responsabile della comunicazione dell’amministrazione cittadina, ha spiegato che il consiglio comunale si riunirà il 4 Giugno per discutere lo studio e che «non ci sono preconcetti al riguardo»: dopo le verifiche potrebbe essere definitivamente fermato come è possibile che venga autorizzata la prosecuzione. Sebbene l’amministrazione Biden stia finanziando la ricerca su diversi interventi climatici, tra cui tecnologie geoingegneristiche che rientrano nella categoria della Solar Radiation Modification (SRM), la Casa Bianca aveva preso le distanze dallo studio californiano, inviando una dichiarazione al New York Times in cui si poteva leggere: «Il governo degli Stati Uniti non è coinvolto nell’esperimento di modifica della radiazione solare (SRM) che si svolge ad Alameda, in California, o in qualsiasi altro luogo».
Greg Goldsmith, decano associato per la ricerca e lo sviluppo presso la Chapman University, aveva fatto notare come il progetto CAARE non menzionasse i suoi potenziali impatti ecologici. «La storia ci ha dimostrato che quando ci inseriamo nella modificazione della natura, ci sono sempre conseguenze indesiderate molto gravi. E quindi, sarebbe prudente ascoltare ciò che la storia ha mostrato e trarne le conseguenze». Non è il solo. David Santillo, scienziato senior di Greenpeace International, si era detto profondamente scettico sulle proposte di modificare la radiazione solare, in quanto le conseguenze sarebbero difficili da prevedere, o anche da misurare: «si potrebbero cambiare i modelli climatici, non solo sul mare, ma anche sulla terraferma. Questa è una visione spaventosa del futuro che dovremmo cercare di evitare a tutti i costi». Sarah Doherty, scienziata atmosferica presso l’Università di Washington e responsabile del programma di schiarimento delle nuvole marine, ha ammesso che potrebbero esserci potenziali effetti collaterali che devono ancora essere studiati, tra cui il cambiamento dei modelli di circolazione oceanica e delle temperature, che potrebbero danneggiare la pesca e che l’illuminazione delle nuvole potrebbe anche alterare i modelli delle precipitazioni, riducendo le precipitazioni in un luogo e aumentandole altrove.
Inoltre, i critici e gli attivisti fanno notare come la Geoingegneria, specie quella che gioca con il fuoco, ovvero con il Sole, oltre che potenzialmente negativa sulla salute del pianeta e di chi vi abita, è un incentivo a non cambiare assolutamente niente nella produzione e nell’organizzazione umana iniqua e non sostenibile. Infatti, se anche la geoingegneria potesse mai funzionare senza alcun impatto sulla Terra, avrebbe il solo scopo di cercare di risolvere gli effetti nocivi generati da un sistema di produzione e sfruttamento ecologico insostenibile e nocivo, senza puntare a modificarlo.
[di Michele Manfrin]
English translate
CALIFORNIA SUSPENDS SRM SOLAR GEOENGINEERING PROJECT OVER POSSIBLE HEALTH EFFECTS
TECHNOLOGY AND CONTROL
15 MAY 2024 – 2.30pm
In Alameda, California, near San Francisco, local officials ordered the interruption of an SRM solar Geoengineering experiment that began last April, the aim of which was to make clouds more reflective so as to artificially decrease heat produced by the sun. The experiment, conducted by researchers from the University of Washington, involved the spraying of tiny particles of sea salt fired at great power from the flight deck of a decommissioned aircraft carrier, the USS Hornet, docked in San Francisco Bay. However, the city of Alameda announced that it had ordered the researchers to stop, citing possible health problems for the population.
The experiment in question is part of the CAARE project (Coastal Atmospheric Aerosol Research and Engagement) and was started on April 2nd. It fell into the category that includes Geoengineering techniques and technologies that aim to reflect solar radiation, Solar Radiation Modification (SRM), one of those considered most controversial due to its invasive impact and unknown ecological and social consequences and repercussions. The organizers of the experiment had decided to maintain maximum secrecy about it for fear that activists could stop it, as has already happened other times in the USA. «City staff are working with a team of biological and hazardous materials consultants to independently evaluate the environmental health and safety of this particular experiment. “The city is evaluating the chemical compounds in the spray to determine whether they are a hazard if inhaled in aerosol form by humans and animals, or by landing on land or in the bay,” Alameda officials wrote. Sarah Henry, communications manager for the city administration, explained that the city council will meet on June 4th to discuss the study and that “there are no preconceptions about it”: after the checks it could be definitively stopped as it is possible that it be authorized the continuation. Although the Biden administration is funding research on several climate interventions, including Geoengineering technologies that fall into the category of Solar Radiation Modification (SRM), the White House had distanced itself from the Californian study, sending a statement to the New York Times in which one could read: «The United States government is not involved in the solar radiation modification (SRM) experiment taking place in Alameda, California, or anywhere else.»
Greg Goldsmith, associate dean for research and development at Chapman University, had pointed out that the CAARE project did not mention its potential ecological impacts. “History has shown us that when we engage in the modification of nature, there are always very serious unintended consequences. And therefore, it would be prudent to listen to what history has shown and draw the consequences.” He’s not the only one. David Santillo, senior scientist at Greenpeace International, said he was deeply skeptical about the proposals to modify solar radiation, as the consequences would be difficult to predict, or even to measure: “climate patterns could be changed, not only at sea, but even on land. This is a frightening vision of the future that we should try to avoid at all costs.” Sarah Doherty, an atmospheric scientist at the University of Washington and manager of the marine cloud clearing program, admitted that there may be potential side effects that still need to be studied, including changing ocean circulation patterns and temperatures, which could harm fisheries, and that cloud lighting could also alter precipitation patterns, reducing precipitation in one place and increasing it elsewhere.
Furthermore, critics and activists point out how geoengineering, especially that which plays with fire, i.e. with the Sun, as well as being potentially negative for the health of the planet and those who live on it, is an incentive to change absolutely nothing in production and in unequal and unsustainable human organization. In fact, even if geoengineering could ever work without any impact on the Earth, it would have the sole purpose of trying to resolve the harmful effects generated by an unsustainable and harmful ecological production and exploitation system, without aiming to modify it.
Source: L’Indipendente





https://www.mondadoristore.it/Scie-guerra-alterazione-Gianni-Lannes/eai979128120216/

Independent journalist Gianni Lannes against chemtrails

The independent journalist Gianni Lannes in a recent photo

“Israel final Holocaust” the book wrote from Gianni Lannes
Dott. Alessio Brancaccio, tecnico ambientale Università degli Studi di L’Aquila, membro della Fondazione Michele Scarponi Onlus, ideologo e membro del movimento ambientalista Ultima Generazione A22 Network per contrastare il Riscaldamento Globale indotto artificialmente dalla Geoingegneria Solare SRM